$29
ATI TEAS 6 Science Study Guide 2
FEMALES
Produce ova (oocytes/egg cells)
Transfer ova to fallopian tubes for
fertilization
Receive sperm from male
Provide a protective, nourishing
environment for developing embryo
External Organs: Labia Majora, Labia Minora, Bartholin's Glands, Clitoris
Labia (both): Close and protect vagina Bartholin's Gland: Secrete lubricating fluid
Clitoris: Contains erectile tissue and nerve endings for sensual pleasure
Internal Organs: Ovaries, Fallopian Tubes, Uterus, Vagina
Ovaries: Female gonads; produce ova, and secrete estrogen and progesterone Fallopian Tubes: Carry mature egg toward uterus; site of fertilization
Uterus: Fertilized egg implants on uterine wall; protects and nourishes developing embryo until birth
Vagina: Muscular tube from cervix to outside of body; receives semen, is site of intercourse, and birth canal
Hormones
Estrogen: Stimulates egg maturation; female sex characteristics
Progesterone: Prepares uterus to receive fertilized egg
FSH: Stimulates oogenesis
LH: Stimulates estrogen production
Oxytocin: Stimulates contraction of uterus and mammary gland cells
Prolactin: Stimulates milk production
Immune System
Function: Protects the body against invading pathogens including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protists. Lymphatic System: Lymph, lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymph nodes.
Skeletal muscle contractions move the lymph one way through the lymphatic system to lymphatic ducts
o Dump back into venous supply via lymph nodes
Red marrow- produces blood cells
Leukocytes- WBC
Lymph Nodes: located in neck, armpit, and groin
Small swellings in the lymphatic system where lymph is filtered and lymphocytes are formed Lymph Tissue: Tonsils, adenoids, thymus, spleen, peyer's patches
5
Tendon: Articulates MUSCLE to BONE
Hyaline Cartilage: Covers articulating surface of bones
Prevents bone on bone grinding
Synovial Joint: Contain lubricating synovial fluid
Pivot Joint: Neck
Ball and Socket Joint: Hip
Hinge Joint: Knee
Osteocytes: Bone Cells
Osteoclast: Multinucleate
o Removes/absorbs bone tissue during growth and healing
Osteoblast: Mononucleate
o Cells that build bone
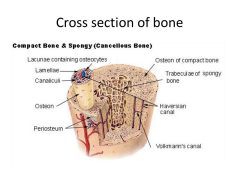
Periosteum: Fibrous sheath that covers bone and contains nerve and blood vessels Osteon: Cylindrical structure that comprise, synthesize, and compact bone Composed of Calcium and phosphate rich Hydroxyapatite embedded in collagen matrix Collagen: Primary structural protein of connective tissue
Canaliculi: Small channel or duct in ossified bone
Cartilage: Tough, elastic connective tissue found in parts of the body (Ear)
Haversian Canal: Channels in bone that contain BV
and Nerves
Lamellae: Layers of the bone, tissues, or cell walls
Lining Cells: Flattened bone cells that come from
osteoblasts
Volkmann Canal: Channels in bone that transmit BV
and communicate with Haversian Canals
Bone Disease
Osteoporosis: causes brittle, fragile bones
Brittle Bone Disease: Group of Diseases that
affect the collagen (defect in the matrix) and results in fragile bones
Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progressive disease the causes joint inflammation and pain
9